What Is a Credit Score?
A credit score is a number that is three numbers long and indicates your creditworthiness in the US. It informs the lenders of your responsibility in the money borrowed. This score is not determined by the amount of credit you make, but by the way you utilize credit in the long term. This number is used by the banks, credit card companies and the lenders to determine whether to grant your application. The more the credit score, the less risk to the lenders. The credit score might seem confusing to the beginners; however, it is just a reflection of your previous financial behavior. Each payment that is made on time contributes towards trust. Any non-payment is detrimental. The credit scores are normally between 300 and 850 in the US system.
The Process of Credit Score calculation

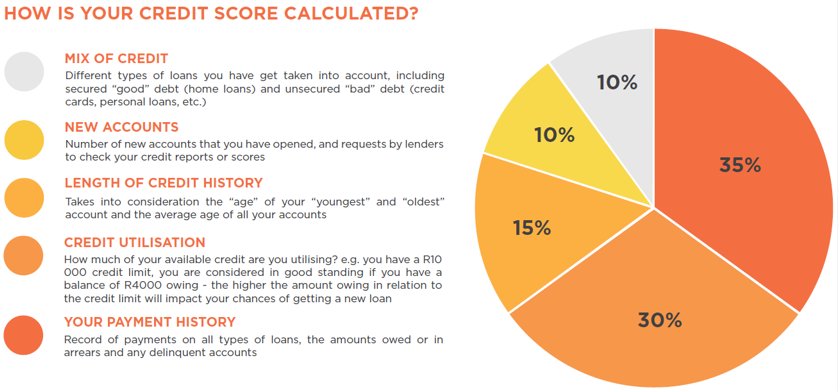
In the USA, credit ratings are computed based on your credit report information. Payment history is the most significant consideration, as it demonstrates whether you pay bills in time. The second significant consideration is the use of the credit available to you, that is, the percentage of the available credit that you utilize. The length of credit history is also important because accounts with longevity are stable. Hard inquiries have an impact on your score because of new credit applications. A minor role is played by credit mix, which entails card ownership and loan possession. This combination of factors gives you a score that can be said to be reflective of your habits. Considerable actions can be felt in the long run. Consistency is stronger than actions, which are short-term.
FICO vs VantageScore
The credit scoring models are the FICO and VantageScore in the United States. Banks, mortgage lenders, and credit card firms are the most common users of FICO. Free credit monitoring sites usually use the VantageScore. The two models are similar in that they utilize the same kind of data yet with a slight difference in the weighting of various factors. FICO concentrates more on the long-term credit behavior. VantageScore will be able to provide a score more quickly to new users. There would be slight variation in scores between the two models, which is normal. The lenders normally define the model used. Novices must concentrate on the acquisition of good habits instead of specific figures.
Credit Bureaus in USA
The United States has three large credit bureaus, including Experian, TransUnion and Equifax. These firms gather and store your credit history. The lenders communicate your payment behavior to one of more of these bureaus. There might be a slight difference in data in each bureau resulting in slight score differences. Accounts, balances, payment history, inquiries are contained in your credit report. The credit score is based on these reports. Reports should be checked frequently and any mistakes detected. Wrong information may negatively score you. The US law provides the option of challenging mistakes to be corrected.
What Affects Score the Most
The largest element influencing your credit score is the payment history, and it comprises approximately 35% of the score. Late payments undermine credibility in no time. Credit utilization is the second factor which is most important and should be maintained to less than 30% level. Wireless credit history enhances your credit score because it demonstrates experience. Multiple credit applications may temporarily reduce your credit score. Diversity of credit is not necessary but was found to be helpful. Settling old accounts may shorten the length of scores. Balances are not needs when it comes to credit building. Good use is always better than often borrowing.
Myths About Credit Score
There are numerous myths that hurt the credit of many people. There is a myth that when somebody looks at his or her score, it goes down- this is not true. The other myth is that having a balance enhances credit which only adds interest expenses. There is an opinion that income influences credit score, which is not true. It is generally thought that closing unused cards will help, but it may damage your score. There is also no harm of paying bills ahead in terms of credit. Credit repair companies too promise immediate things, which is not realistic. Credit construction is not a quick-fix. Knowing the truth helps beginners to avoid making errors.
How to Check Score for Free
The USA has free credit score checking without breaking your credit. There are numerous credit card applications and banks that offer free score-checking. Platforms such as credit karma and Experian are free. Looking at your score is a mild question and does not make a difference. You are also entitled to get your credit report once a year in each of the bureaus. Your score allows you to monitor your progress and identify problems in the initial stages. Frequent inspections create financial consciousness. Novices must monitor their score every month. The initial step towards improvement is knowledge.
Final Beginner Checklist
To write off the beginners in the USA, a credit construction checklist is sufficient. Take out one starter credit account. Use less than 30% of your limit. Do not late on any bill. Do not apply to more than one card. Keep accounts open long-term. Check credit reports on a regular basis. Disregard rumors and emphasize on facts. Be patient and consistent. Another skill is credit building; it is an art that enhances financial freedom and is a long-term skill. Small intelligent actions will make great credit tomorrow.
FAQ’s
1. What is a good credit score in the USA?
In the United States, a credit score of 670 or above is considered good. This range usually qualifies you for better loan approvals and lower interest rates. Scores above 740 are viewed very positively by lenders.
2. Can I have multiple credit scores at the same time?
Yes, you can have multiple credit scores. Your FICO score and VantageScore may differ slightly. Also, each credit bureau can show a different score based on reported data.
3. Does closing a credit card hurt my credit score?
Yes, closing a credit card can lower your score. It reduces your total available credit and can shorten your credit history. That’s why keeping old accounts open is often better.
4. How often does my credit score update?
Credit scores usually update every 30–45 days, depending on when lenders report data to credit bureaus. On-time payments reflect gradually, not instantly.
5. Can I build credit if I’m new to the USA?
Yes, immigrants and newcomers can build credit in the USA. Secured credit cards, student cards, and credit builder loans are common starting options.


